In recent years, the world has seen a growing interest in space exploration and satellite technology. Satellites have become an integral part of our daily lives, providing communication, navigation, and earth observation services. While there are thousands of satellites in space right now, building and launching your own personal satellite is still a daunting task for many people. However, with the availability of low-cost components and easy-to-use development tools, it is now possible to build a mini satellite at home. In this article, we will guide you through the process of making a mini satellite and launching it into space.
Step 1 Planning and Research: The first step in building a mini satellite is to plan and research the project. This involves identifying the purpose and requirements of the satellite, selecting the components and software, and determining the launch vehicle and regulatory requirements. Some of the factors to consider during this phase include the satellite's size, weight, power requirements, communication system, sensors, and data storage. It is also important to research the various satellite building companies and "cubesat kits" available in the market and decide on the most suitable option based on your needs and budget.
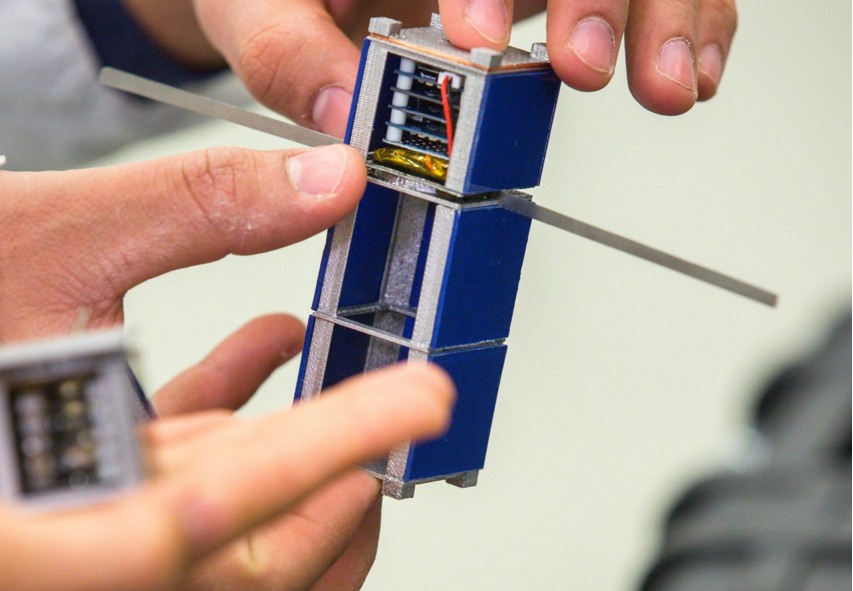
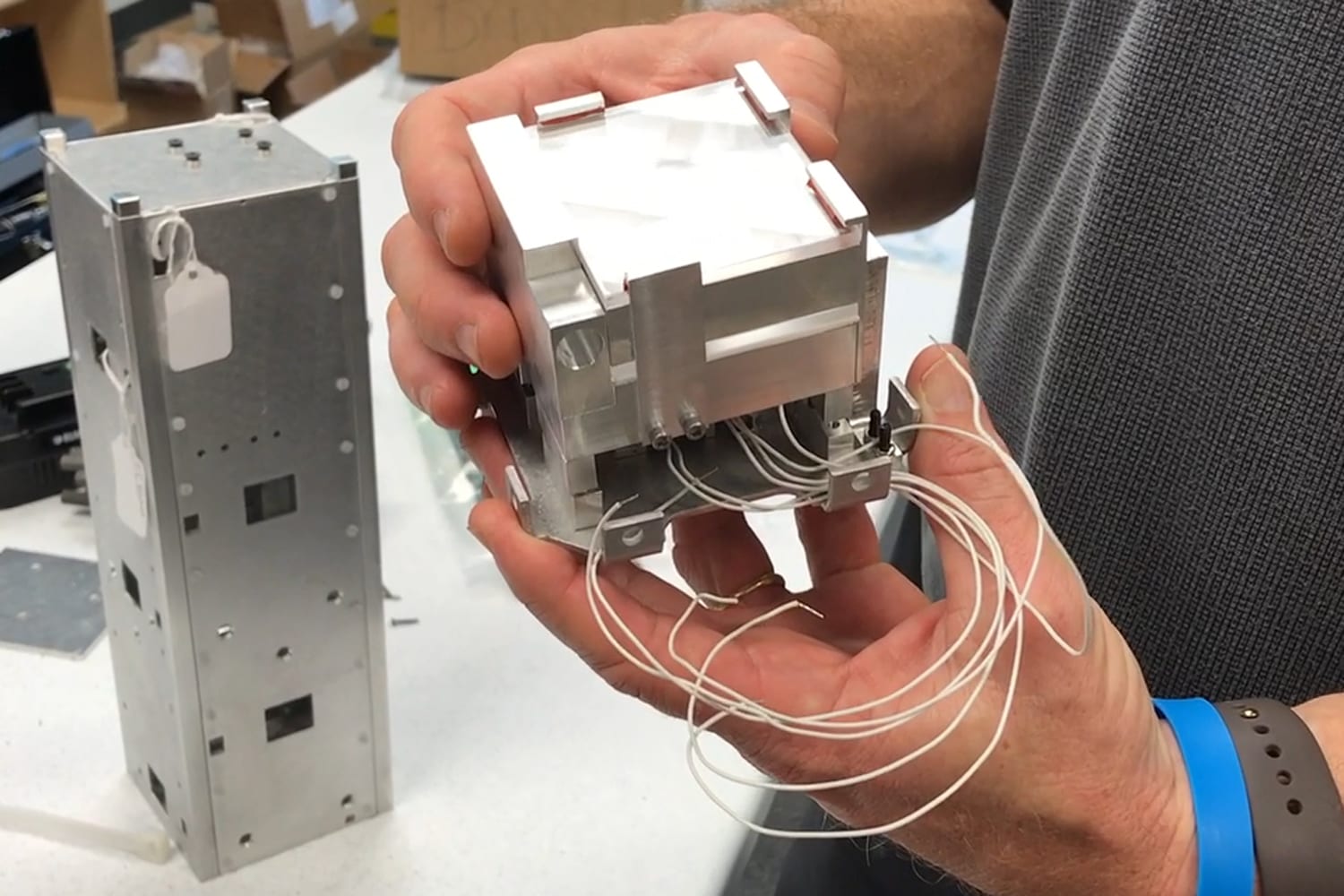
Step 2 Building the Satellite: Once you have planned and researched the project, the next step is to build the satellite. The structure of a basic mini satellite consists of a chassis, power system, communication system, sensors, and a data storage device. The chassis serves as the frame and provides support for the other components. The power system includes batteries, solar panels, and a power management module to regulate the voltage and current. The communication system comprises an antenna, transceiver, and a ground station for sending and receiving data. The sensors can include cameras, temperature sensors, and accelerometers, among others, to collect data from the environment. The data storage device stores the collected data for later analysis.
Several companies offer these kits, which typically include all the necessary components to assemble a small satellite, including solar panels, batteries, antennas, and communication systems. Some popular CubeSat kit providers include CubeSatShop, Pumpkin Inc, and Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems.
Alternatively, you can also build your own custom satellite using off-the-shelf components and open-source software. This approach requires more technical expertise and knowledge of electronics and programming, but it allows for greater flexibility in terms of satellite design and functionality.
One popular platform for building DIY satellites is the Arduino, a microcontroller board that can be programmed to control various sensors, actuators, and communication systems. Several resources are available online that provide step-by-step instructions and code examples for building Arduino-based satellites, including the Tiny Space Program Guide and the 'RocketBuilder' website.
Step 3 Programming the Satellite: Programming the satellite involves writing the code to control the various components and perform the intended tasks. The programming language used depends on the hardware and software components selected for the satellite. Some of the popular programming languages used in satellite development include C++, Python, and Arduino. The code should be optimized for the limited resources of the satellite, such as memory, processing power, and communication bandwidth.
Step 4 Testing and verification: Testing and verification are critical steps in satellite development to ensure that the satellite functions as intended and meets the regulatory requirements. The satellite should be tested in various environments, such as thermal vacuum chambers, vibration tables, and electromagnetic interference chambers, to simulate the conditions it will face in space. The satellite's communication system should also be tested with a ground station to verify its performance and data transmission. Once the testing is complete, the satellite should be verified to ensure that it meets the regulatory requirements for launch.
Step 5 Launching the Satellite: The final step in building a mini satellite is launching it into space. Launching a satellite requires a rocket or a launch vehicle that can carry the satellite into orbit. The cost of a satellite launch can vary widely depending on the launch vehicle and the desired orbit. The cost of a satellite launch can range from a few hundred thousand dollars to tens of millions of dollars. Once the satellite is in orbit, it can be operated and controlled remotely from the ground station.
Permission to Launch a Satellite Before launching a satellite, it is important to obtain the necessary permissions and regulatory approvals. In most countries, launching a satellite requires approval from the government or a regulatory agency. The regulatory requirements can vary widely depending on the country and the intended orbit. For example, launching a satellite into the lowest orbit requires less regulatory approval than launching a satellite into a higher orbit. The regulatory approval process can take few weeks to several months.
Once you have received the necessary permissions, it is time to begin preparing for the launch. You will need to purchase a rocket that can carry your satellite into orbit or borrow a rocket from companies which offer satellite launch services.
There are several companies that offer satellite launch services, including SpaceX, Arianespace, United Launch Alliance, and Rocket Lab, among others. These companies have the expertise and resources to launch a satellite into orbit and ensure its safe operation.
One of the notable private satellite launch service providers in India is the Indian company Skyroot Aerospace. Founded in 2018, Skyroot Aerospace is a startup that aims to develop and launch rockets that can carry small satellites into space in reasonable price. The company is headquartered in Hyderabad and has a team of experienced professionals, including former ISRO scientists and engineers. Another Indian private space company that offers satellite launch services is Agnikul Cosmos. Agnikul is a Chennai-based startup that is developing a rocket called Agnibaan, which can carry satellites weighing up to 100 kg. The company aims to provide a flexible and affordable launch service for small satellites. Agnikul Cosmos has also signed agreements with several companies for the launch of their satellites.
Before selecting a satellite launcher company, it is important to consider factors such as cost, reliability, and availability of launch opportunities. Some companies specialize in specific types of launches, such as low Earth orbit or geostationary orbit, while others offer a range of launch services.
Once a satellite launcher company has been selected, the process of launching a satellite involves several stages, including mission planning, satellite integration and testing, launch vehicle integration, and launch operations. It is important to work closely with the launcher company to ensure that all requirements and specifications are met throughout the process. In the next blog we'll discuss the DIY satellite launching and BalloonSat(This is a type of DIY satellite that is launched using a weather balloon) in detail.
In summary, launching a satellite requires careful planning, technical expertise, and a significant investment of time and resources. However, with the availability of cubesat kits and other DIY satellite resources, it is now more accessible than ever for individuals and small organizations to launch their own satellites into space. With the right tools and knowledge, it is possible to explore and study the cosmos from the comfort of your own home.
If you want to build one, there are several rocket building companies that can provide rockets for satellite launches. You will need to research which rocket will be best suited for your particular satellite, taking into account factors such as weight and size.
The cost of a rocket can vary widely, depending on the size and capabilities of the rocket. It is important to budget for this expense, as well as the cost of the launch itself. The cost of launching a satellite can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the type of launch and the rocket used.
Once you have secured a rocket and a launch date, it is time to prepare your satellite for launch. This will involve testing all of the satellite's systems to ensure that they are functioning properly. You will also need to program your satellite, using a programming language such as Python or C++. Programming your satellite is a crucial step, as it will allow you to control your satellite's movements and collect data from its sensors.
In terms of the structure of a basic mini satellite, there are several components that are essential to any satellite. These include the power system, which can be solar panels or batteries; the communication system, which allows the satellite to send and receive data; and the payload, which is the equipment that the satellite is carrying, such as a camera or a sensor. The structure of a satellite must be designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space, including extreme temperatures and radiation.
Some of the basic uses of satellites include communication, navigation, weather monitoring, and remote sensing. Satellites are used to transmit data around the world, allowing people to communicate with one another and access information from anywhere. They are also used to provide precise location information for navigation purposes, as well as to monitor weather patterns and natural disasters. Remote sensing satellites are used to collect data about the Earth's surface, including information about vegetation, water resources, and climate.
There are many resources available to help you build your own satellite at home. The Tiny Space Program Guide, available online, provides step-by-step instructions for building a basic satellite using a CubeSat kit. The CubeSat Shop offers a range of kits and components for building your own satellite. You can also find information and resources on websites such as satellite.space and rocket builder simulation online.
In conclusion, building and launching a personal satellite is a complex and challenging endeavor that requires significant planning, resources, and technical expertise. However, with the right tools and resources, it is possible to build a mini satellite at home and launch it into space. From securing the necessary permissions to designing and programming the satellite, each step of the process is critical to success. By following the guidelines outlined in this article and utilizing available resources, you can build your own satellite and make your mark in the world of space exploration.
Building a mini satellite at home is a challenging but rewarding project that can provide a great learning experience for those interested in space technology. With the availability of affordable and accessible resources, such as CubeSat kits, it is now possible for individuals and small organizations to launch their own satellites into space. However, it is important to note that launching a satellite requires obtaining the necessary permissions and licenses from regulatory bodies, as well as adhering to strict safety protocols.
Furthermore, building a mini satellite is not just a fun hobby, but it also has practical applications in various fields, including weather forecasting, navigation, communication, and scientific research. By building their own mini satellite, individuals can contribute to the advancement of technology and exploration of space.
Lastly, it is worth mentioning that while building a mini satellite at home is a great learning experience, it is important to also acknowledge the efforts of satellite building companies and private businesses that invest significant resources and expertise in developing the materials and technologies used in space rockets and satellites. Their contributions have made it possible for us to explore space and gain a better understanding of the universe.
Building a mini satellite at home is a challenging yet rewarding project that offers a great opportunity to learn about space technology and contribute to scientific research. With the right resources, knowledge, and permissions, anyone can launch their own satellite into space and explore the vast expanse of the universe.




No comments: