What Is Binary Ripple Counter?
In the field of digital electronics, counters play a crucial role in controlling and sequencing the operations of electronic circuits. A binary ripple counter is a type of electronic counter that counts a series of binary numbers in sequence. It is widely used in electronic devices that require the counting of a certain number of events, such as digital clocks and timers.
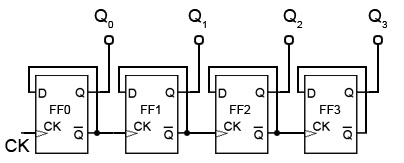
A binary ripple counter is a type of asynchronous counter, which means that the clock signal is applied only to the first flip-flop in the series, and the output of each flip-flop, in turn, triggers the following flip-flop.
Types of Binary Ripple Counters
There are two main types of binary ripple counters: the asynchronous binary ripple counter and the synchronous binary ripple counter.
1. Asynchronous Binary Ripple Counter
In an asynchronous binary ripple counter, the outputs of each flip-flop are not directly connected to the next flip-flop's clock input. Instead, the clock signal is applied to the first flip-flop, and its output is used to trigger the clock input of the next flip-flop.
This type of binary ripple counter is relatively simple and straightforward to implement. However, it suffers from a limitation in the maximum speed of operation, as the propagation delay between each stage leads to a cumulative delay in the output signals. As a result, it is not suitable for counting a large number of events in a short period.
2. Synchronous Binary Ripple Counter
In a synchronous binary ripple counter, the output of each flip-flop is connected directly to the next flip-flop's clock input. In this way, all flip-flops change state simultaneously, rather than sequentially as in the asynchronous counter.
This eliminates the cumulative delay problem of the asynchronous counter and allows it to operate at much higher speeds. However, it is more complex to implement and requires additional control and synchronization signals.
Advantages of Binary Ripple Counters
1. Simplicity: Binary ripple counters are relatively simple to implement and require fewer components than other types of counters.
2. Flexibility: Binary ripple counters can count a wide range of events and can be easily customized by adding or removing flip-flops.
3. Accuracy: Binary ripple counters provide accurate and reliable counting of events, ensuring the precise execution of electronic circuits.
Disadvantages of Binary Ripple Counters
1. Limited speed: Asynchronous binary ripple counters have a limited speed of operation, which makes them unsuitable for counting a large number of events in a short period.
2. Cumulative delay: The multiple flip-flops in asynchronous binary ripple counters lead to a cumulative delay in the output signals, making them less efficient than synchronous binary ripple counters.
3. Synchronization issues: Synchronous binary ripple counters require additional control and synchronization signals, making them more complex to implement and troubleshoot.
Conclusion
In conclusion, binary ripple counters are an essential component in digital electronics, providing accurate and reliable counting of events. They are available in different types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right type of binary ripple counter depends on the specific requirements of the electronic circuit, and all factors should be carefully considered before selecting a particular type.<check>Selecting a particular type of binary ripple counter can be challenging, as it requires a thorough understanding of the circuit's specifications and operational requirements. Some factors to consider include the number of events to count, the speed of operation, the precision required, and the type of electronic devices that the counter will be used with.
Overall, binary ripple counters continue to play a crucial role in digital electronics, providing reliable and accurate counting of events in a wide range of electronic circuits. By understanding the different types and their advantages and disadvantages, designers can choose the right type of binary ripple counter for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of the electronic circuit.
The selection of the right type of binary ripple counter is essential in ensuring that the electronic circuit is working efficiently and effectively. If the counter is not functioning properly, it may result in errors in the overall functioning of the circuit. Therefore, factors such as the number of events to count and the speed of operation must be carefully considered while selecting the type of binary ripple counter.
Asynchronous binary ripple counters are simple to implement and use fewer components, making them a popular choice for simple digital circuits. However, they have a limited maximum speed of operation, which makes them unsuitable for counting large numbers of events in a short period. Also, because the output signals travel through multiple flip-flops, there may be a significant delay in the output signals. Therefore, asynchronous binary ripple counters are usually only suitable for basic digital applications that do not require high frequency or precise timing.
Synchronous binary ripple counters, on the other hand, have far fewer limitations in their maximum speed of operation and are more precise in their timing. They are, however, more complex to implement and require additional synchronization and control signals. Synchronous binary ripple counters are an excellent choice when high-frequency counting is needed, and precision is necessary, but they may not be the best option for simpler digital circuits as they have more complex implementation requirements.
In conclusion, selecting the right type of binary ripple counter is essential in ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the circuit's operation. By understanding the differences in the various counter types, designers can choose the best-suited type for their specific application. Additionally, conducting appropriate testing and verification checks can help ensure that the binary ripple counter is performing accurately within the target electronic circuit.
Binary ripple counters have been around for several decades and are an essential component of digital electronics. The earliest examples of ripple counters were based on electromechanical relays and were used in early electromechanical computers.
The first electronic binary ripple counter is attributed to John Bardeen and Walter Brattain, who invented the first transistor in 1947. The invention of the transistor paved the way for the development of more advanced digital technology, which made it possible to build more efficient and faster binary ripple counters.
Over time, various improvements and modifications have been made to binary ripple counters, resulting in the various types of counters that are available today. Advances in semiconductor technology have allowed designers to create counters with higher precision and faster speeds of operation, making them more practical for various digital applications.
In summary, the history of binary ripple counters is long and rich, and these counters have been continuously refined and improved over the years to meet the demands of the rapidly evolving digital electronics industry.

No comments: